Statutory Section
In FY 2024-25, we continued to strengthen our on-ground execution by integrating sustainability into everyday operations. In energy and emissions, we deepened our focus on efficiency and advanced our transition toward cleaner power sources across all our plants.
On the waste front, 'Zero Waste to Landfill' remained a top priority, while in packaging, we made significant progress towards circularity by scaling up the use of recyclable materials and reducing the environmental footprint of our product designs.
Our water strategy comprising conservation, rainwater harvesting, and responsible usage, helps us move closer to our Net Zero Water goals. All these areas, our teams continue to push boundaries, guided by science.


We're committed to tackling climate change to help create a healthier, more sustainable future. Our approach combines energy efficiency, emissions reduction, and a steady shift towards clean energy sources. These actions are closely aligned with our business goals and are carried out in full compliance with environmental regulations and standards.
In FY 2024-25, we utilized approximately 232.464 TJ of energy across all our Indian plants, with 33% sourced from renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
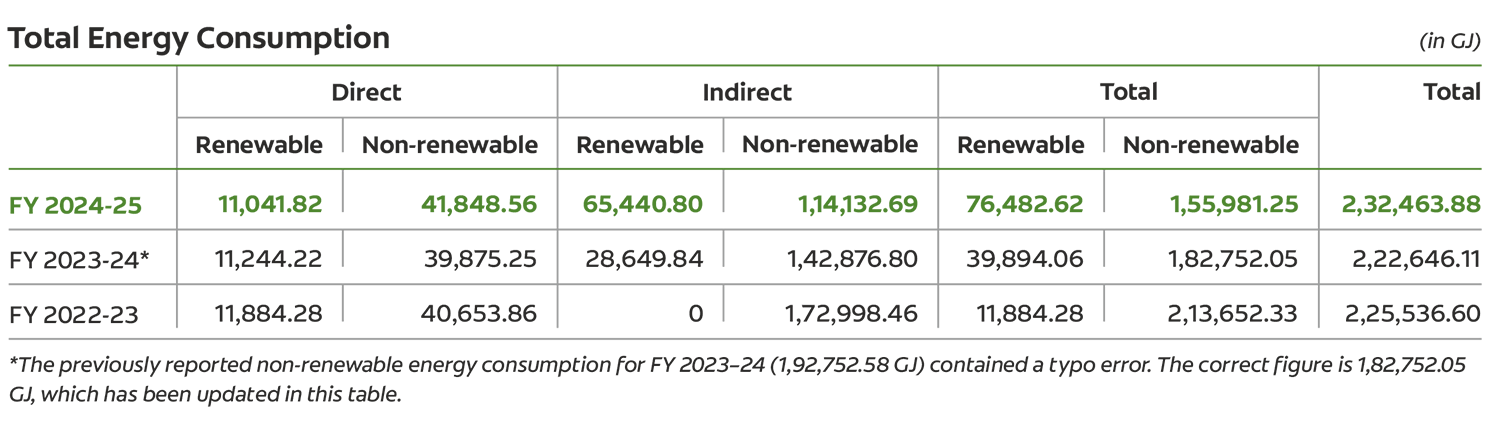
Total energy consumption increased by 4.4% compared to the previous year, driven by a 9% rise in production volumes. Despite the higher production output, we effectively managed energy usage through targeted efficiency initiatives and sustained energy-saving measures across all four manufacturing facilities. The energy mix has also showed a positive trend with the share of renewable energy in total consumption increasing by 91.7% and that of non-renewable energy decreasing by 14.6% over the previous year.
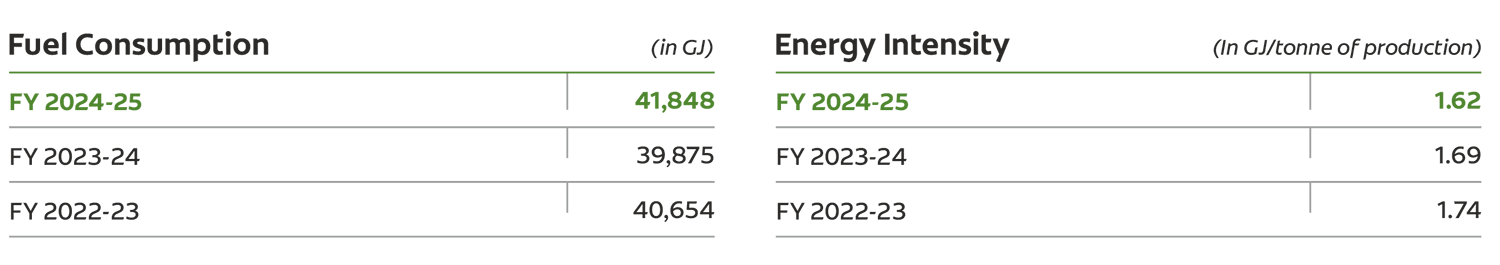
The rise in energy consumption is attributed to increased production activity. However, through focused energysaving initiatives implemented across all plants, we successfully maintained energy intensity at optimized levels, reinforcing our commitment to operational efficiency.


The plant enhanced energy efficiency through several upgrades, including the installation of electronically commutated blowers in AHUs (Air handling units), saving approximately 1,31,475 kWh annually. Motion sensors introduced at key locations further saved around 228 kWh. A new energy-efficient boiler burner added savings of 7,920 kWh/year, while a newly installed ozonator delivered an additional 1,000 kWh/year in savings.
The plant implemented a comprehensive energy conservation program, including lighting upgrades, energy analytics, and employee-led 'Energy Treasure Hunt' workshops. These initiatives collectively reduced energy consumption by 6%, saving 12,03,563 kWh. Solar energy generation (1 MW on-site) and a hybrid power purchase agreement contributed 40.10% of total power needs. Investments of INR 1.74 crore into new solar projects, HVAC improvements, and a small boiler are expected to save 1,50,000 kWh annually. An external energy audit is also underway to unlock further opportunities.
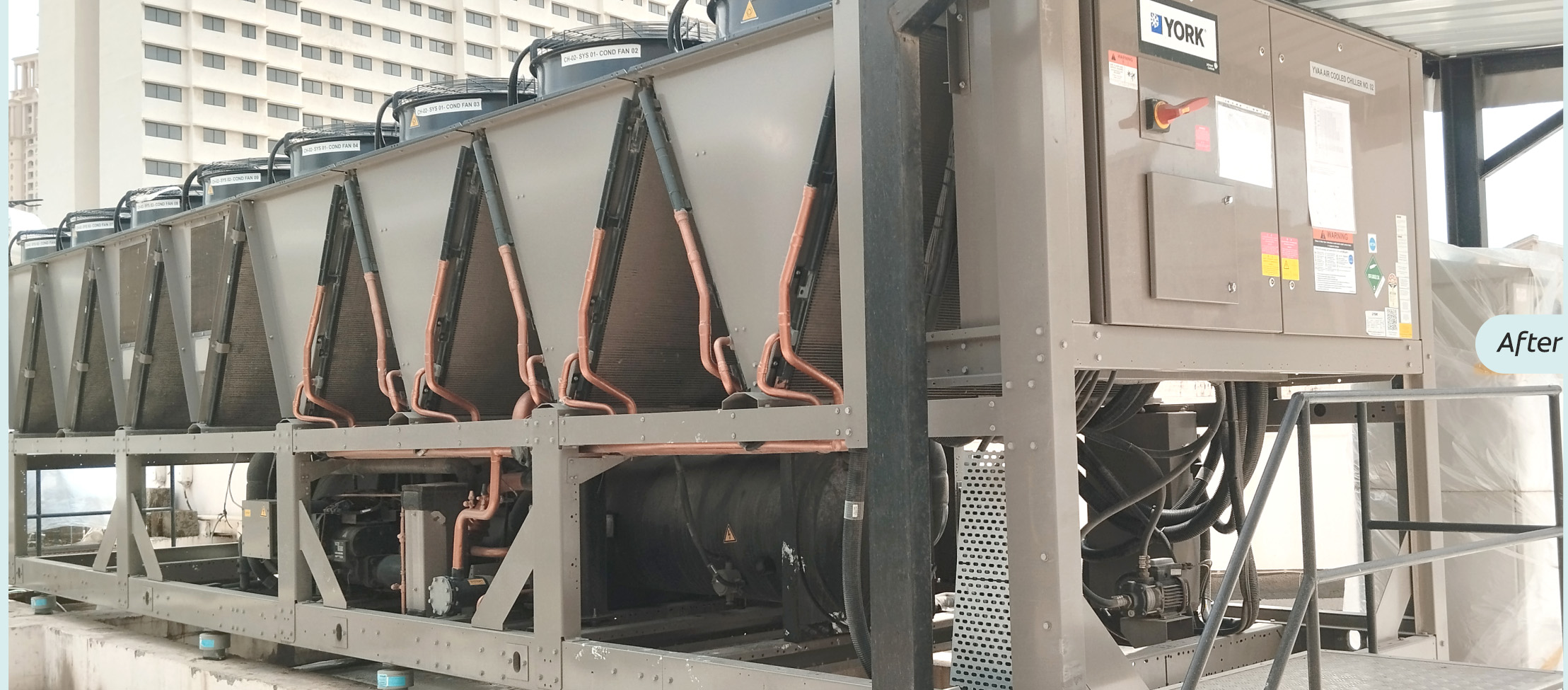

The in-house 1.788 MW solar plant enabled savings of 1,653 MWh from the grid. Renewable energy procurement through PPAs accounted for 6,058 MWh, together covering 51% of the plant's energy needs.
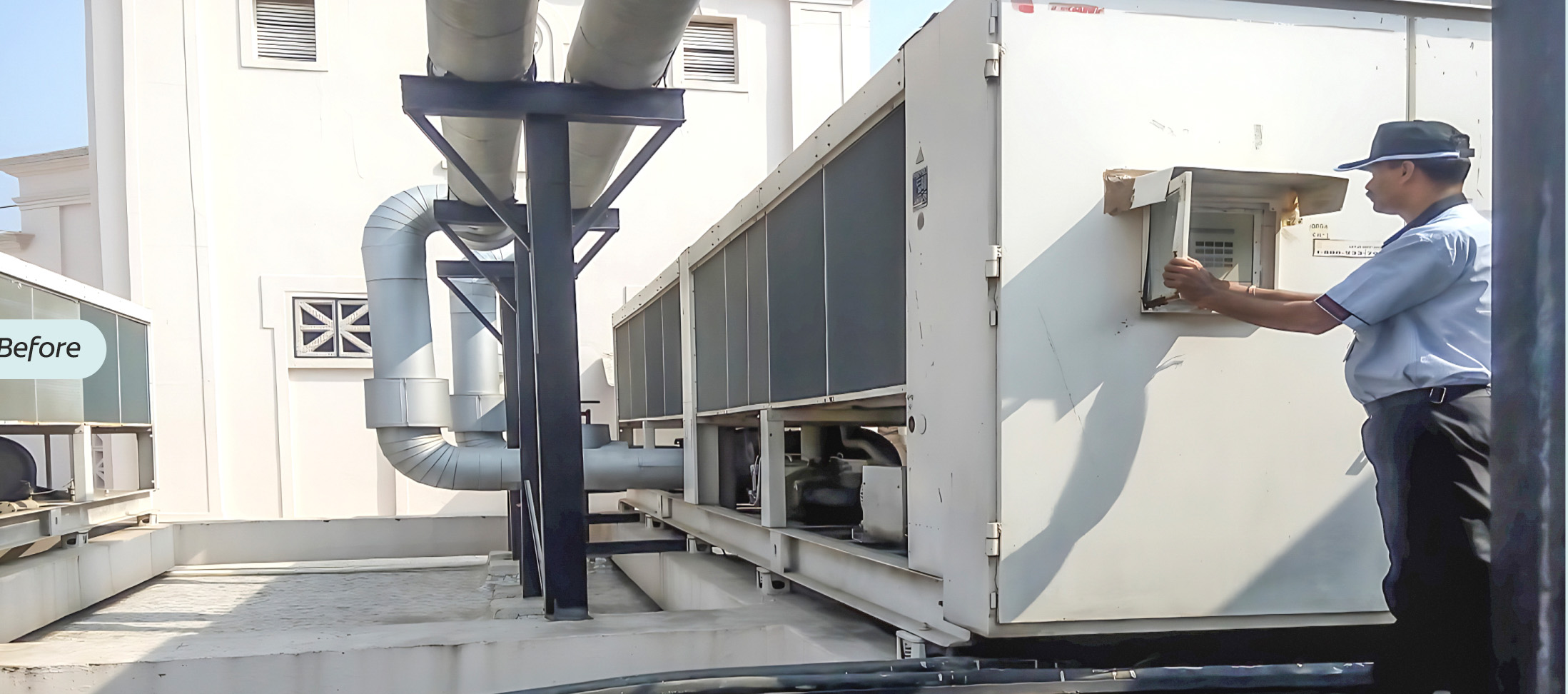
The plant replaced fixedspeed chillers with magnetic bearing chillers equipped with variable drives, resulting in significant improvements in energy efficiency
For more details about this initiative, please refer to the 'Manufacturing Excellence' section of this report on page 10
The Head Office in Mumbai replaced decades-old chillers with energy-efficient models using R513A refrigerant, a greener alternative. This upgrade led to a 3.08% reduction in annual power consumption, aided by optimizing Micro Lab HVAC loads onto the new chillers.
Since 2013, Colgate-Palmolive (India) Ltd. has adopted the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) green building rating system by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) to help reduce exposure to water and climate-related risks while creating healthier, more comfortable work environments.
In India, our manufacturing plants at Sri City and Sanand have successfully earned LEED Gold certification.
Cut GHG Emissions (Scope 1 & 2) by 42% by 2030 (from 2020 baseline)
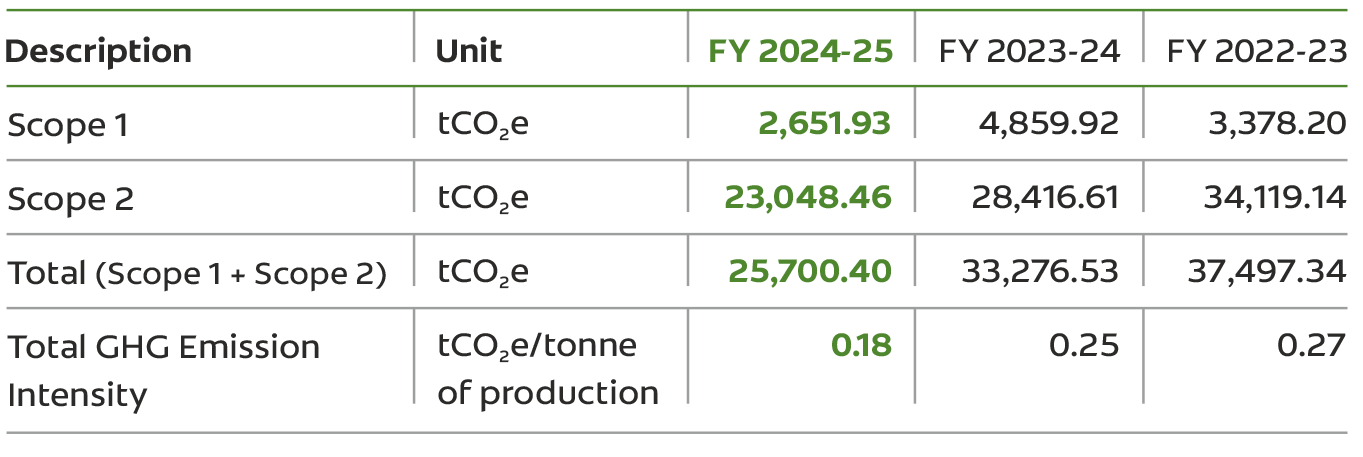
In FY 2024-25, we observed a 22.7% decrease in our carbon emissions, as compared to year's reporting of 25,700.40 tCO e. This reduction can be 2 attributed primarily to a higher portion of renewable electricity usage in plant operation and replacement of diesel with PNG (Piped Natural Gas).
The table below illustrates the changes in our Scope 1 and 2 emissions, as well as our GHG intensity, over the last three years.


In FY 2024-25, our consumption of CFC-11 eq. Ozone Depleting Substances was 1.0756 MT. We plan to adopt the latest pollution control equipment to ensure higher energy efficiency and reduce fugitive emissions.
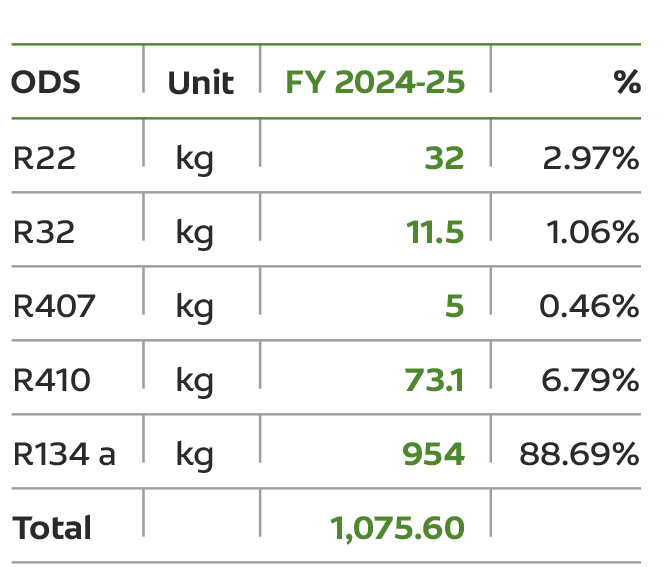
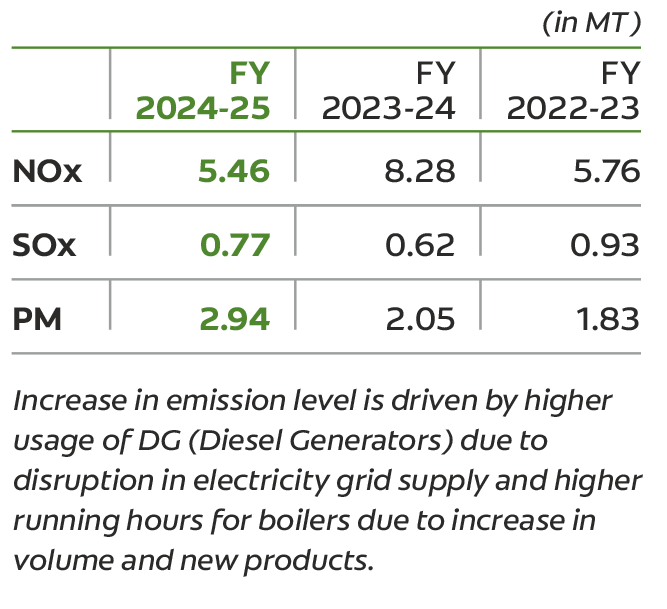

Our waste management strategy follows circular principles, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing social benefit.
This year, we upheld our TRUE© Certification for Zero Waste across all four plants, with plans underway to include the Head Office in the certification process.
We continue to strengthen our systems to reduce, reuse and recover waste. Waste from manufacturing - whether due to raw material contamination or machine inefficiencies - is systematically classified, segregated, and analyzed. Through advanced monitoring, trend tracking and targeted interventions, we're optimizing resource use and making faster strides toward our long-term goals.

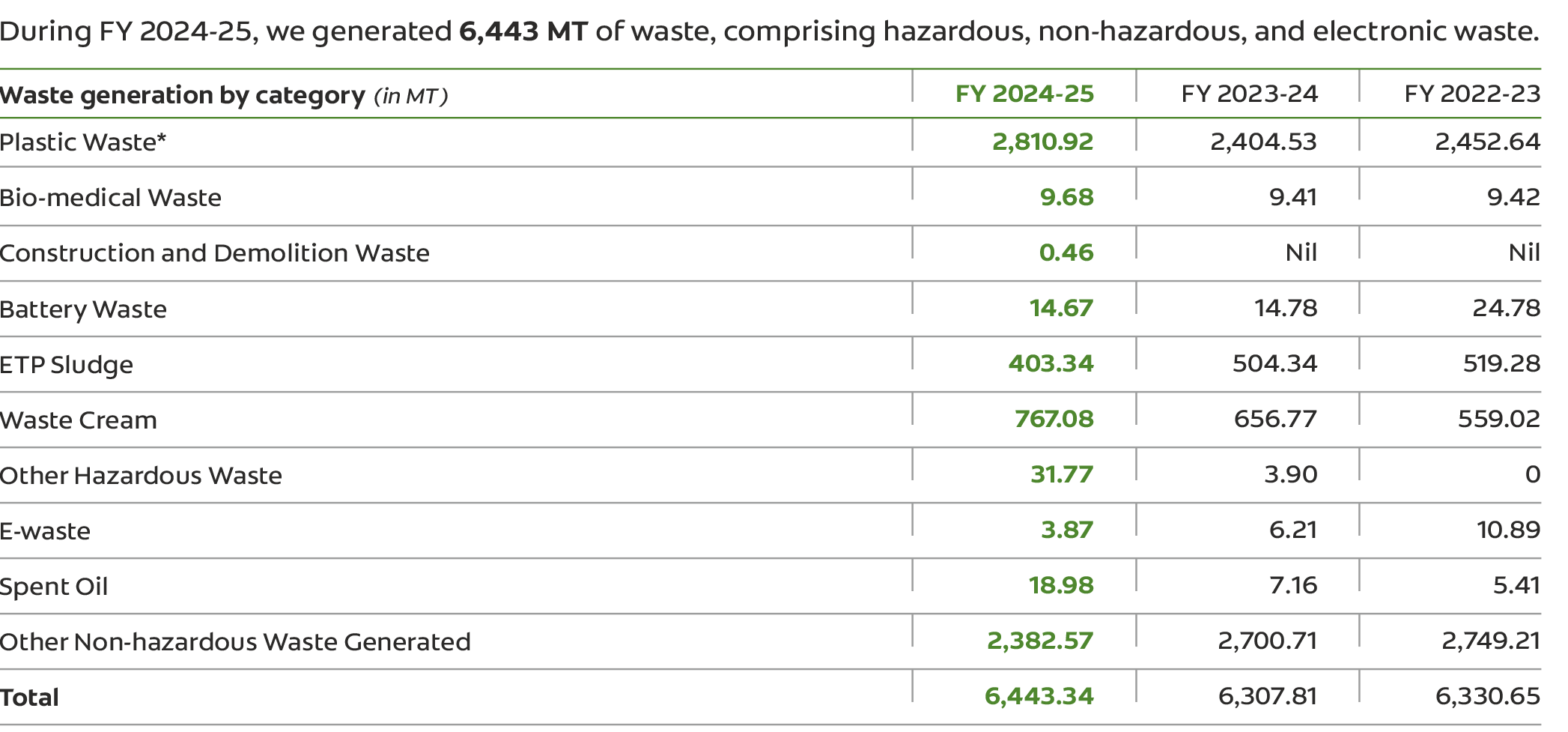 *Plastic Waste data for FY 2023–24 has been updated to include previously omitted figures from one of the plants, which were missed during last year's
computation.
*Plastic Waste data for FY 2023–24 has been updated to include previously omitted figures from one of the plants, which were missed during last year's
computation.
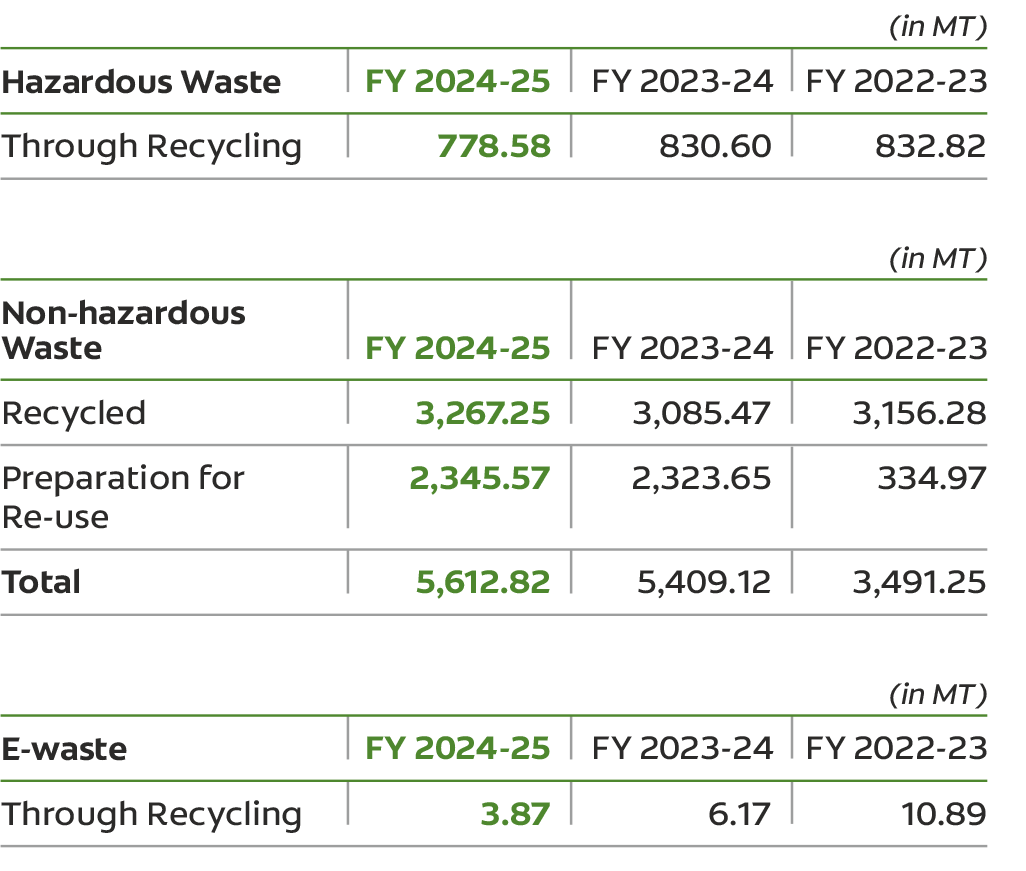
We successfully diverted 6,395.27 MT of waste in FY 2024-25, of this 4,049.70 MT was recycled and 2,345.57 MT was reused.
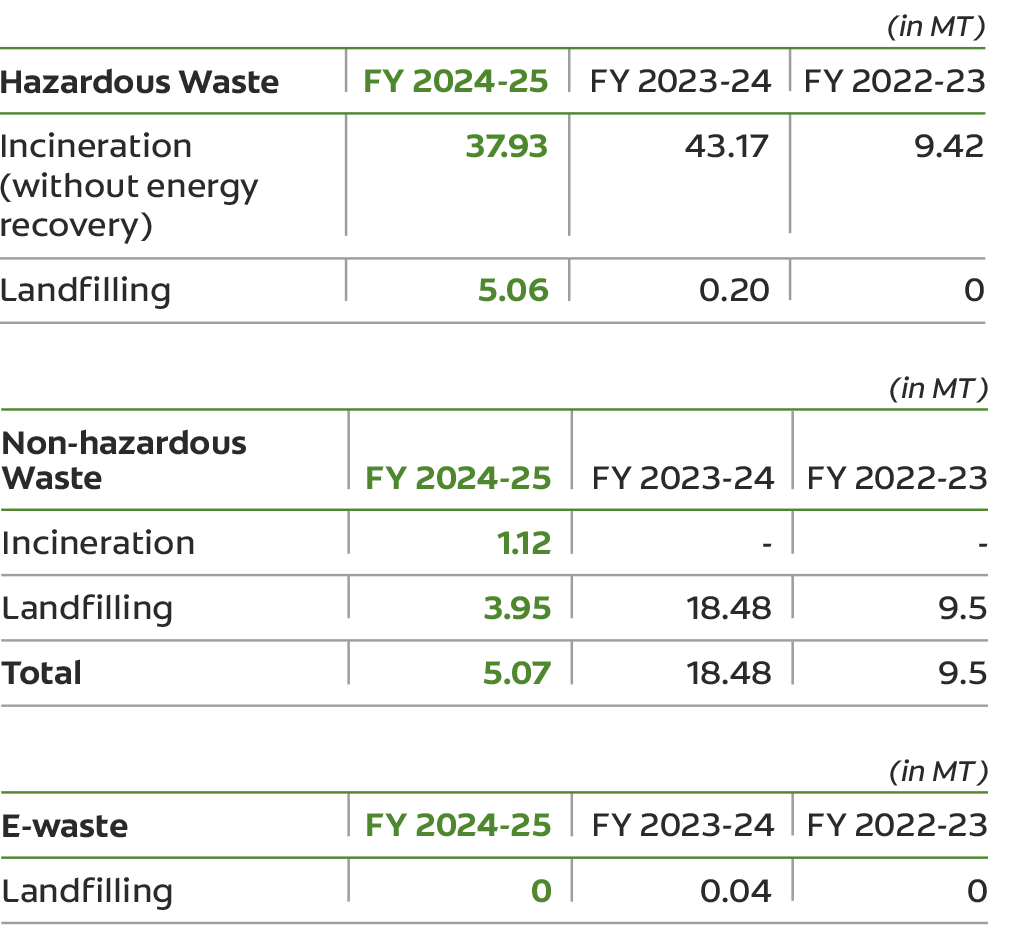
Recycling of wood and food waste helped reduce total landfill waste by 51.24%.


The team has also phased out single-use items, replacing plastic bottles and paper cups with glassware, significantly cutting down on disposable waste. Another standout initiative is the shift from individual dustbins to shared waste stations in every pantry, reducing plastic liner usage and encouraging collective ownership of waste disposal.
In line with the 'Save Paper' initiative, the office has transitioned to e-certificates, digital gate passes, and paperless documentation. Going beyond waste reduction, the team has organized e-waste recycling drives and used clothes collection efforts, reinforcing a culture of sustainability across the workplace.

| Make all of our packaging reusable, recyclable or compostable by end of 2025. | Continue to achieve over 100% of plastic waste collection under EPR every year. |

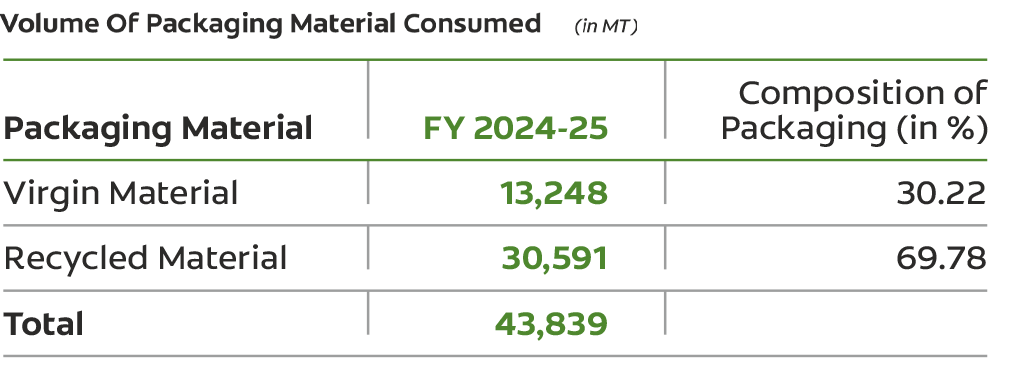
We continue to invest in sustainable packaging to minimize waste and maximize recyclability. Our target is to make all of our packaging recyclable, reusable, or compostable by the end of 2025. We also remain consistent in achieving 100% plastic waste collection under India's Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) each year.
By analyzing packaging trends and adopting targeted interventions, we are actively reducing our waste footprint and driving responsible waste management. A key focus area is innovation, which includes developing alternative materials and smarter designs to reduce dependence on virgin resources and enable a more circular value chain.
We pioneered the launch of India's first-of-its-kind recyclable toothpaste tube made from HDPE*, a material known for its high recycling rate globally.
Creating a squeezable tube from HDPE posed technical challenges due to its rigidity, but Colgate-Palmolive Company engineers overcame this by layering HDPE laminates at varying thicknesses; thereby delivering a recyclable tube with the same functional performance.
We shared this breakthrough openly, even with industry peers, to help accelerate the global shift to recyclable tubes. Today, we remain committed to transitioning 100% of our toothpaste portfolio in India to recyclable tubes by 2025.
During FY 2024-25, 91% of our total packaging by weight was recyclable. While we continue to pursue solutions for our 'flexible' and other non-recyclable packaging, which pose industry-wide challenges, achieving our goal of making all packaging recyclable, reusable, or compostable may extend beyond our original 2025 timeline.

Access to safe water, sanitation, and hygiene is a key pillar of our water stewardship. We aim for Net Zero Water by advancing efficiency, minimizing waste, and using tools like WRI's Aqueduct to identify stress-prone areas. Despite challenges in water-scarce regions like Sanand and Baddi, we continue to drive freshwater conservation and efficient water treatment practices.
Three out of four of our plants — Sri City, Sanand and Goa — have achieved Net Zero Water through harvesting initiatives.
Across locations, we use smart monitoring systems and promote responsible water treatment to ensure availability for communities, underscoring our commitment to long-term water sustainability.
We utilize various water sources, including groundwater, municipal water supply, industrial corporation sources, and rainwater. In FY 2024-25, we replenished over 21,590 KL of rainwater from all our operational locations. A total of 429 million litres of water has been replenished in the states of Maharashtra & Rajasthan since 2018, via various CSR programs.
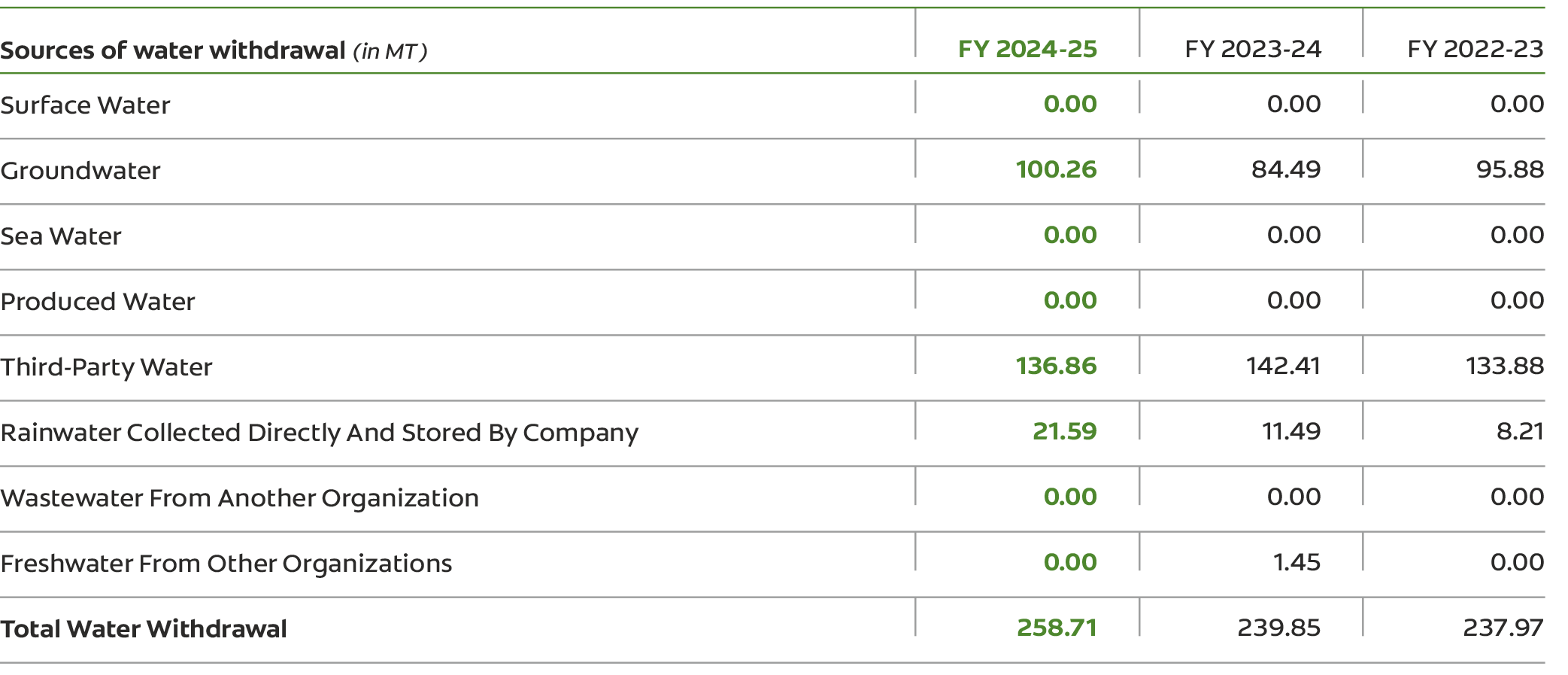
Our water withdrawal is almost equal to our water consumption.
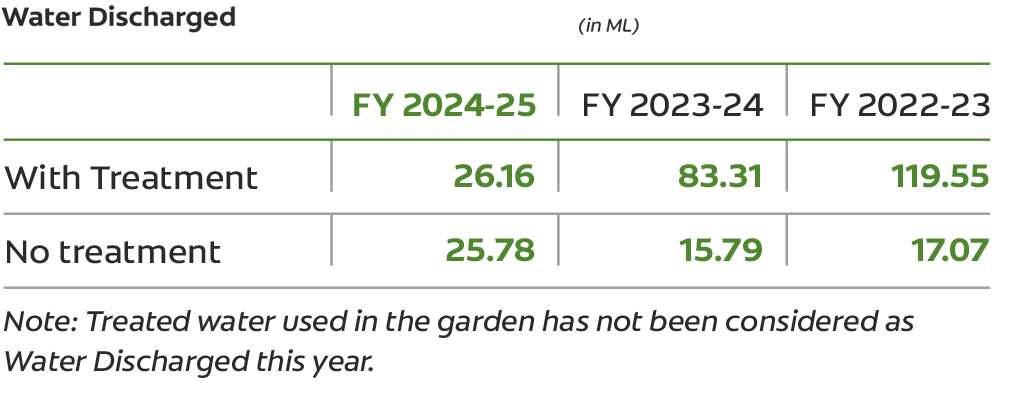
We leverage advanced technology for continuous monitoring of wastewater quality, helping minimize environmental impact. Our facilities are equipped with three stage treatment plants—featuring tanks, clarifiers, mixers, and filters—that ensure effective removal of impurities. Key parameters such as pH, BOD, COD, color, fluorides, and TSS are closely tracked to meet regulatory norms. Treated water is reused for cooling towers, boilers, and gardening, supporting our circular water approach.
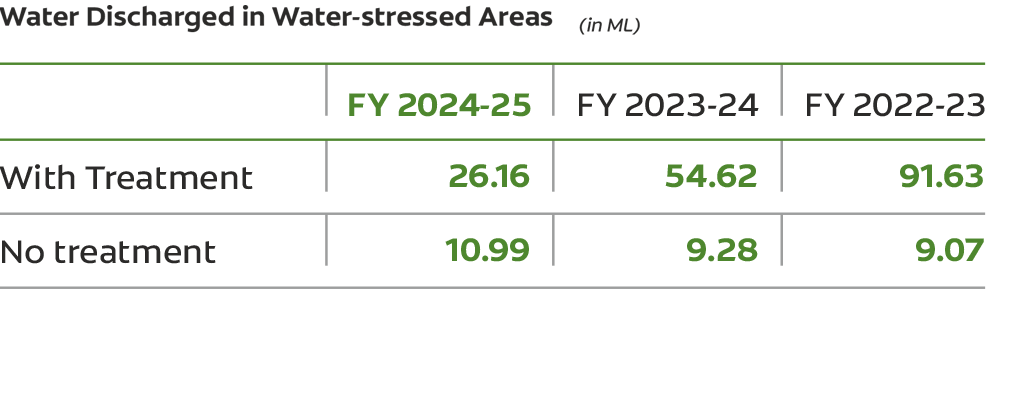
In FY 2024-25, discharge water was reduced by 47.58% compared to previous year due to consideration of gardening water as a part of recycling instead of discharge. Our Baddi plant is required to send its effluent water to the Central Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP) for processing, resulting in the site being unable to achieve Net Zero Water status.


A cutter pump mechanism was introduced to separate solids before they enter the treatment plant. This simple yet effective upgrade led to multiple benefits: a notable reduction in solid waste generation, lower consumption of treatment chemicals, and improved quality of treated water.
Sludge from the decanter — typically with 55–65% moisture — is now dried using open pans, resulting in drier solids that are easier and more cost-effective to transport and co-process. Manual bagging is currently done in smaller lots, with a plan underway to optimize the drying and collection cycle.
By adopting slurry pumping and pan drying methods, the plant has reduced its dependency on chemicals and lowered decanter energy use, thereby creating a more sustainable sludge management system with lower environmental impact and operational costs.
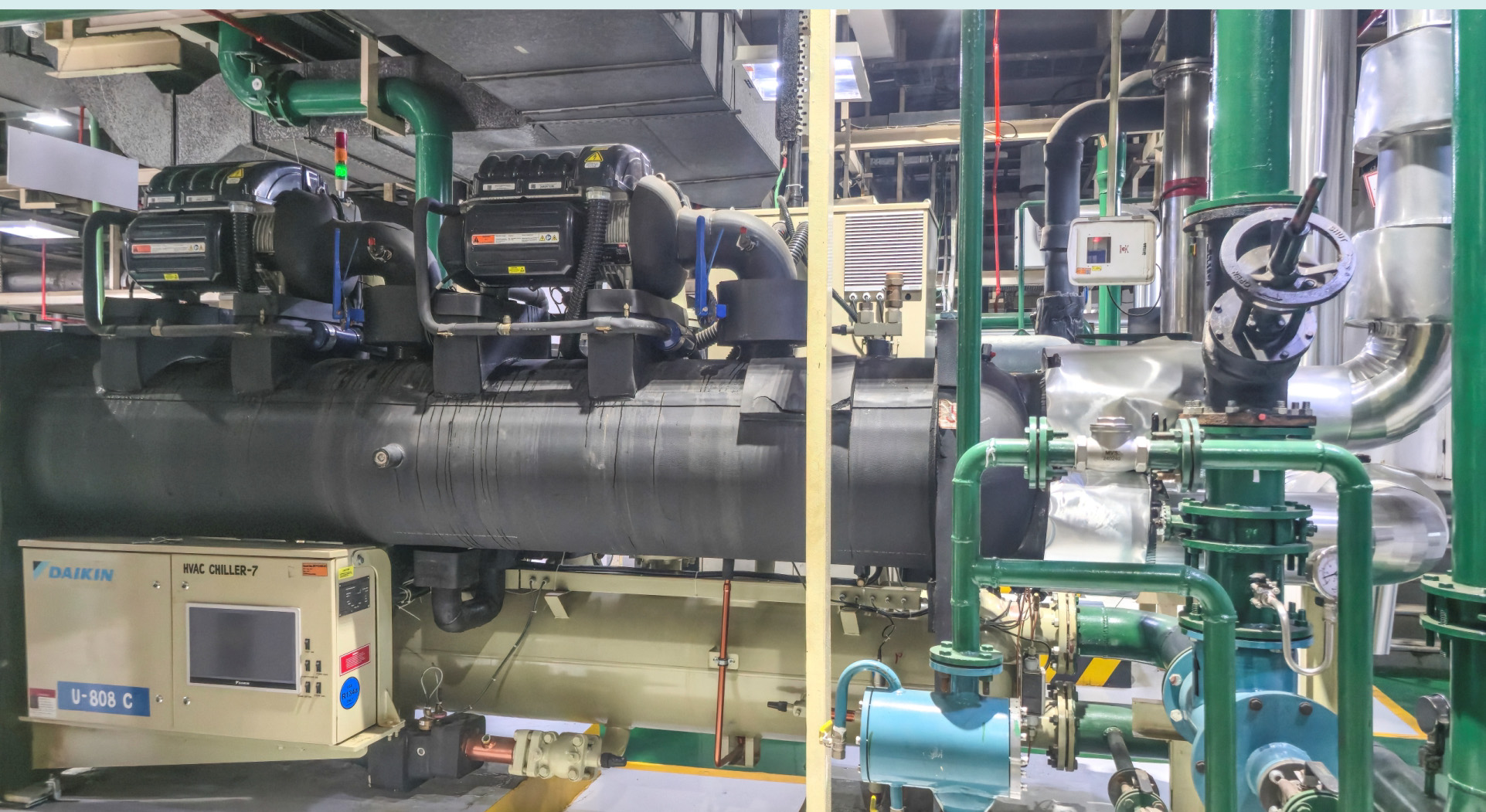



At the Sri City plant, a demand flow solution was implemented to optimize chiller performance by maintaining the required flow and temperature at the delivery point. This synchronized subsystems into a virtual single chilled water loop, solving low temperature difference (delta T) issues and increasing deliverable tonnage. The initiative led to reduced energy consumption, less wear and tear, extended equipment life, and improved indoor comfort. In FY 2024-25, it resulted in energy savings of 3,39,165 kWh.
Additionally, the use of energy-efficient magnetic bearings at the Goa plant reduced chiller energy consumption by 40%. This initiative delivered a 7% overall energy saving and will save approximately INR 1 crore annually for the plant.